Even With Recent Rises, Auto Insurance Is More Affordable Than During Most of Century to Date

You read that right. As a percentage of median household income, personal auto insurance premiums nationally were more affordable in 2022 (the most recent data available) than they have been since the beginning of this century.
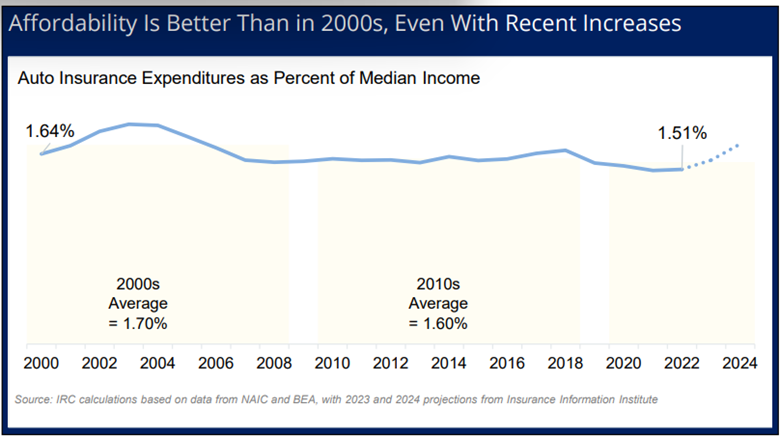
And even the premium increases of the past two years are only expected to bring affordability back into the 2000 range, according to the Insurance Research Council (IRC).
A new IRC report – Auto Insurance Affordability: Countrywide Trends and State Comparisons – looks at the average auto insurance expenditure as a percent of median income. The measure ranges from a low of 0.93 percent in North Dakota (the most affordable state for auto insurance) to a high of 2.67 percent in Louisiana (the least affordable).
The pain is real
This is not to downplay the pain being experienced by consumers – particularly those in areas where premium rates have been rising while household income has been flat to lower. It’s just to provide perspective as to the diverse factors that come into play when discussing insurance affordability.
Between 2000 and 2022, median household income grew somewhat faster than auto insurance expenditures, causing the affordability index to decline from 1.64 percent in 2000 to 1.51 percent in 2022. In other words, auto insurance was somewhat more affordable in 2022 than in 2000.
“With the recent increases in insurance costs, affordability is projected to deteriorate in 2023 and 2024,” said Dale Porfilio, FCAS, MAAA, president of the IRC and chief insurance officer at Triple-I. “The affordability index is projected to increase to approximately 1.6 percent in 2023 and 1.7 percent in 2024, a significant increase from the low in 2021 but still below the peak of 1.9 percent in 2003.”
In other words, we’ve been here before; and, if risks and costs can be contained, so can premium growth in the long term.
Cost factors vary by state
Auto insurance affordability is largely determined by the key underlying cost drivers in each state. They include:
- Accident frequency
- Repair costs
- Claim severity
- Tendency to file injury claims
- Injury claim severity
- Expense index
- Uninsured and underinsured motorists
- Claim litigation.
These factors vary widely by state, and the IRC report looks at the profiles of each state to arrive at its affordability index.
Reducing risk and costs is key
Porfilio noted that “while state-level data cannot directly address affordability issues among traditionally underserved populations, collaborative efforts to reduce these key cost drivers can improve affordability for all consumers.”
Continued replacement-cost inflation is likely to maintain upward pressure on premium rates. Tariffs could exacerbate that trend, as well as hurting household income in areas dependent on industries likely to be affected by them.
At the same time, some states are working hard to ameliorate other factors hurting affordability. Florida, for example, was the second least affordable state for auto insurance in 2022; however, the state has made recent progress to reduce legal system abuse, a major contributor to claims costs in the Sunshine State. In 2022 and 2023, Florida passed several key reforms that have led to significant decreases in lawsuits. As a result, insurers have been writing more business in the state after a multi-year exodus. This increased competition puts downward pressure on rates, which should be reflected in the IRC’s next affordability study.
Learn More:
IRC Report: Personal Auto Insurance State Regulation Systems
Florida Reforms Bear Fruit as Premium Rates Stabilize
What Florida’s Misguided Investigation Means for Georgia Tort Reform
Florida Bills Would Reverse Progress on Costly Legal System Abuse
Inflation Continues to Drive Up Consumers’ Insurance Costs
Improved Commercial Auto Underwriting Profitability Expected After Years of Struggle
Louisiana Is Least Affordable State for Personal Auto Coverage Across the South and U.S.
Georgia Is Among the Least Affordable States for Auto Insurance
Report: No-Fault Reforms Improved Michigan’s Personal Auto Insurance Affordability
Auto Insurers’ Performance Improves, But Don’t Expect Rates to Flatten Soon

